
Secure Credit Union Website Hosting That Just Works
Credit unions and other financial institutions are facing growing pressure



Keyloggers remain a major threat in 2025, widely used by attackers to silently capture passwords, inputs, and system activity, and by security teams to assess defense gaps during ethical red team engagements. Keyloggers can operate below traditional detection layers, enabling them to be a highly effective and dangerous credential harvesting technique. Keylogging is likely to be used to acquire credentials for new access opportunities when OS Credential Dumping efforts are not effective, and may require an adversary to intercept keystrokes on a system for a substantial period of time before credentials can be successfully captured (MITRE ATT&CK 1 & 3, 2025).
Additionally, they can serve as powerful assets in ethical security testing. Keyloggers are capable of silently capturing everything from passwords to command-line commands with little chance of detection. This guide explains what keyloggers are, how attackers use them, and most importantly, how to detect, and defend your systems against them.
A keylogger is software or hardware that secretly records keystrokes pressed on a keyboard, or otherwise every keystroke stored in a keyboard buffer. Often used maliciously, keyloggers store or send captured data to hackers, who analyze it to steal credentials and access secure systems, usually without the victim knowing (Fortinet, 2025).
As you can see in the image below, some of the keylogger’s goals are to steal credentials, monitor commands/behaviors, and enable lateral movement.

However, InfoSec professionals also employ keyloggers responsibly during penetration tests and red team operations to expose vulnerabilities. Keyloggers function at various system layers: application, operating system, kernel, and hardware — each progressively more difficult to detect. Regardless of type, their core goal is to quietly capture your keystrokes.
Software keyloggers are malicious programs that are installed directly on the target system to capture keystrokes and send or store this data for attackers. They are among the most prevalent methods attackers use to intercept user input (Fortinet, 2025).
Software-Based Keylogger types include:
Hardware-based keyloggers are physically inserted between a keyboard and the computer (via USB or PS/2 ports). Often disguised as adapters, hardware-based keyloggers operate on the hardware level, making them hard to detect with antivirus tools. They store keystroke data locally for later attacker retrieval (SentinelOne, 2025).
Hardware-Based Keylogger Types Include:
Preventing unauthorized physical access is critical to mitigating hardware keylogger threats. Establish rigorous organizational BYOD policies and otherwise strong controls to restrict physical access to devices and ports (SentinelOne, 2025).
Key Croc: A smart USB keylogger developed by Hak5, equipped with penetration testing tools, remote access, and payload capabilities that trigger multi-vector keylogging attacks. It emulates trusted USB devices such as keyboards, storage, and Ethernet adapters to avoid detection and can be controlled remotely through a web interface, making it a powerful tool for cyber attackers and penetration testers alike (Hak5).
O.MG Elite Cable: A covert USB cable masquerading as a standard charger or data cable, embedding an advanced keylogging implant within. It offers features like Wi-Fi control, encrypted command-and-control communication, geo-fencing, and self-destruct mechanisms, providing attackers with stealthy control and data exfiltration options (Hak5).
By understanding these devices and their sophisticated functions, organizations can better recognize the threat landscape and reinforce physical security measures to protect sensitive input data.
Chat With Our Cybersecurity Team Our Cybersecurity Solutions
Defending against malware starts with knowing how threats may arrive. Keyloggers don’t magically appear; hackers use a variety of ways to sneak them onto systems.

Ways Keyloggers Can Enter Systems:
Understanding the ways hackers can gain access to your system can help you prioritize prevention and monitoring.
See exactly where your defenses stand and uncover hidden gaps before attackers do. Take 5 minutes to evaluate your initial security posture with our FREE RISE Foundations Assessment — your first step toward stronger, smarter protection.
Start Your FREE RISE Assessment
To better understand attacker behavior and strengthen defense posture, security teams often rely on the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Key techniques associated with keyloggers include:
Mapping these behaviors can help support prioritized incident response (Messham, 2025).
Even advanced keyloggers leave clues.
Watch for:
Use a combination of process monitoring, network analysis, and log review to find hidden keyloggers (Messham, 2025).
Whether you’re securing desktops and servers, these foundational steps help reduce exposure to keyloggers and similar threats.
Strengthen security with these best practices:
At DataYard, we partner with teams to build tailored cloud cybersecurity strategies that fit your unique environment and risk profile. Whether you’re just starting to tighten controls or are ready for proactive threat detection, our experts are here to help simplify the process and prioritize what matters most.

If you’d like to explore practical ways to enhance your cybersecurity defenses, feel free to reach out anytime for a no-pressure conversation about your security goals.
If you suspect a keylogger is active on your system, act swiftly and methodically:
The faster you’re able to isolate and respond, the more you’ll limit damage and shorten recovery time.
Want expert guidance to help prevent this from happening again? We’re here to help.
Connect With Our Cybersecurity Experts
Keyloggers are sophisticated tools that often disguise themselves as legitimate software and operate with high system privileges, making them exceedingly difficult to detect and remove (Bhardwaj & Goundar, 2020). It is crucial to regularly assess and test the effectiveness of your security controls in order to understand your ability to defend against clandestine attacks, such as keylogging, and to improve your defensive measures effectively.
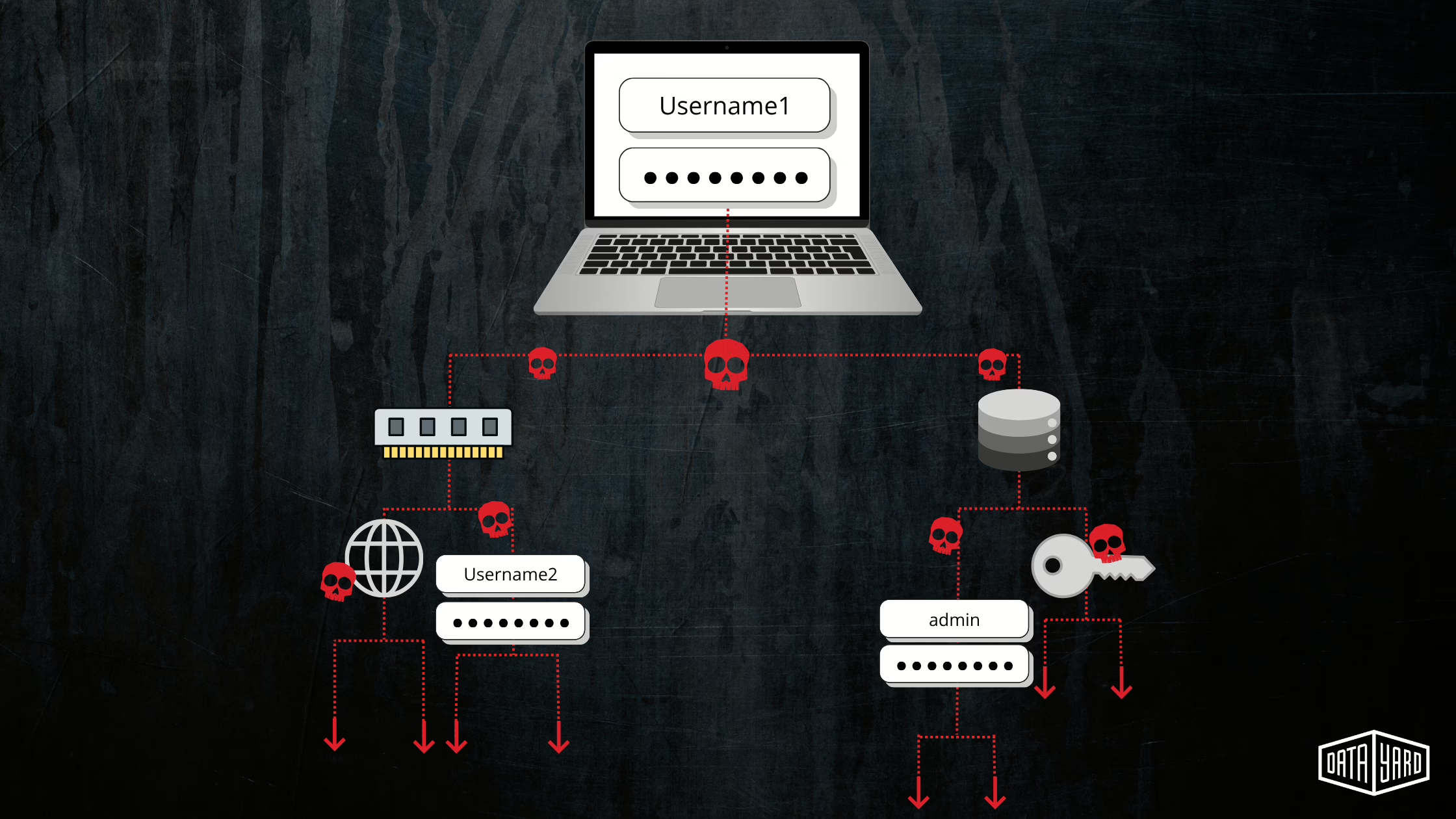
How to test keyloggers:
Understanding keyloggers — how they operate, how they infiltrate, and how to detect and defend against them — is vital in maintaining a secure system. Staying vigilant with updates, monitoring, and employee training can significantly reduce risk.
With DataYard’s managed cloud infrastructure, logging, and endpoint visibility, your environment can be centrally enforced without compromising performance.
DataYard’s Cloud Management Solutions
Review your security posture with DataYard’s RISE Foundations Assessment, a complimentary 5-10 minute evaluation offering personalized reports and actionable recommendations.
If uptime, security, and performance matter to your business, partnering with the right cloud security experts can make all the difference.
Contact Us:
Email: [email protected]
Phone: 937-226-6896 option 2
Disclaimer
This blog post is intended for educational and informational purposes only. The techniques, tools, and references discussed, particularly those related to keylogger development, detection, or testing, are shared to improve awareness and strengthen cybersecurity defenses. Any attempt to replicate, deploy, or experiment with these tools should only be done within explicitly authorized environments for ethical testing, research, or red team operations.
Unauthorized use of keyloggers or malware violates legal and ethical standards and may result in severe consequences, including criminal charges. DataYard disclaims all responsibility for misuse of the information provided. Always consult with qualified security professionals before applying these practices to your environment.
References

Credit unions and other financial institutions are facing growing pressure
Cloud cost optimization in 2026 isn’t just about cutting spend

Phishing remains one of the most dangerous cyber threats facing