
Secure Credit Union Website Hosting That Just Works
Credit unions and other financial institutions are facing growing pressure

If your website or application slows or fails when demand spikes, you need scalable cloud services — a practical approach to cloud scalability that keeps systems running efficiently and controls costs.
Scalable cloud services combine the infrastructure, architecture, and operational practices that allow your systems to expand or contract based on demand — without rebuilding from scratch or overspending to allow for peak capacity 24/7.
Without scalability, increased usage spikes from marketing campaigns, product launches, or viral content can overwhelm systems.
The result? Slow pages, failed checkouts, or downtime when it matters most.
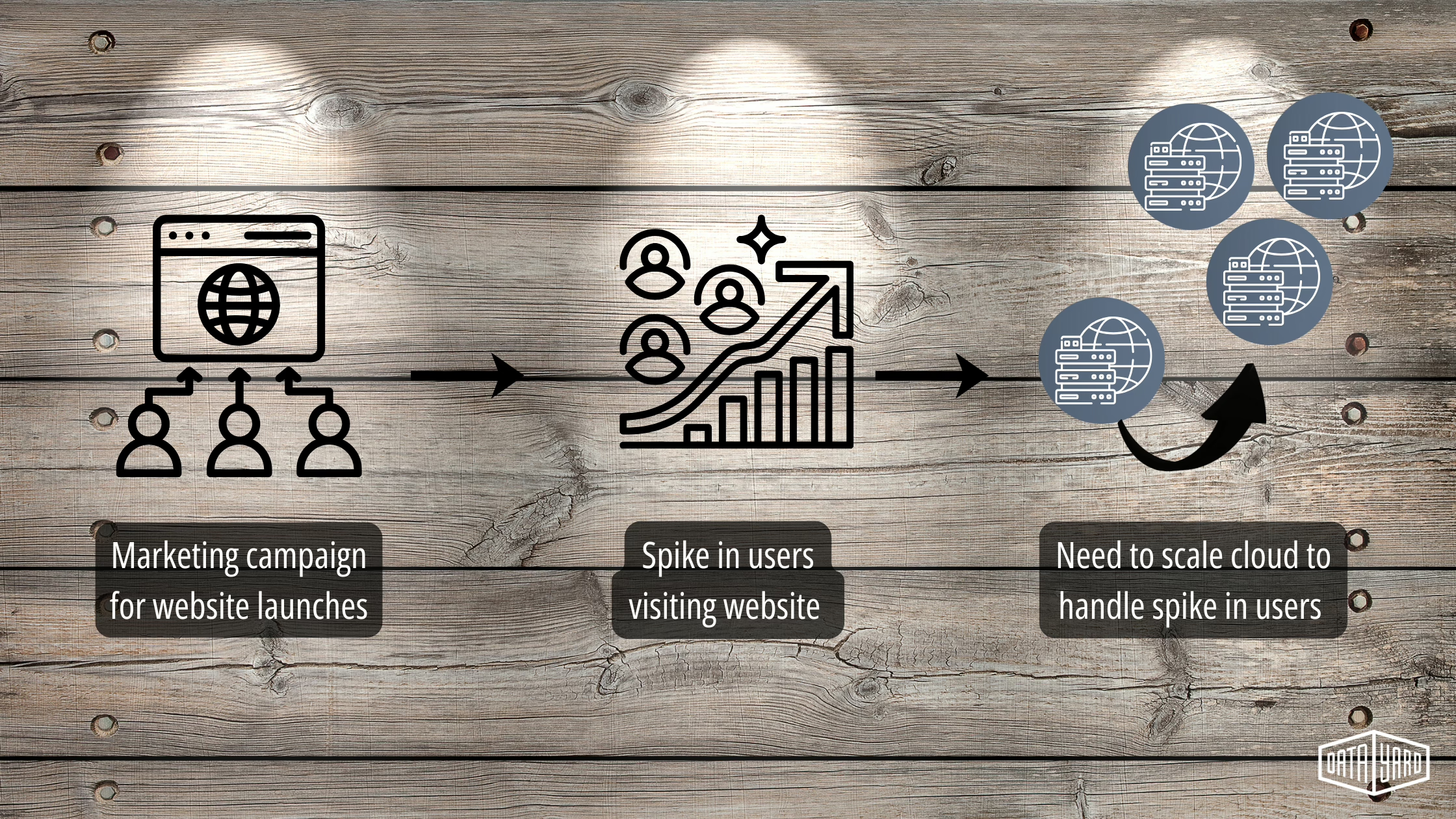
Having a scalable cloud design ensures that:
As CloudZero puts it:
“Good scalability protects you from future downtime and ensures the quality of your service.”
Before you design a scalable cloud architecture, understand the two primary types of scaling: vertical scaling and horizontal scaling. Each approach changes how your cloud resources and systems respond to workload growth, and they each affect cost, performance, and operations.
For many organizations, the outage was a wake-up call about centralization risk: when core DNS and edge services go dark, sites and services worldwide can suddenly become unreachable. If you’re unsure whether your website or third-party tools depend on Cloudflare, a quick audit can reveal single points of failure and help prioritize fixes.
Before planning your architecture, it’s important to understand the two main cloud scaling models:
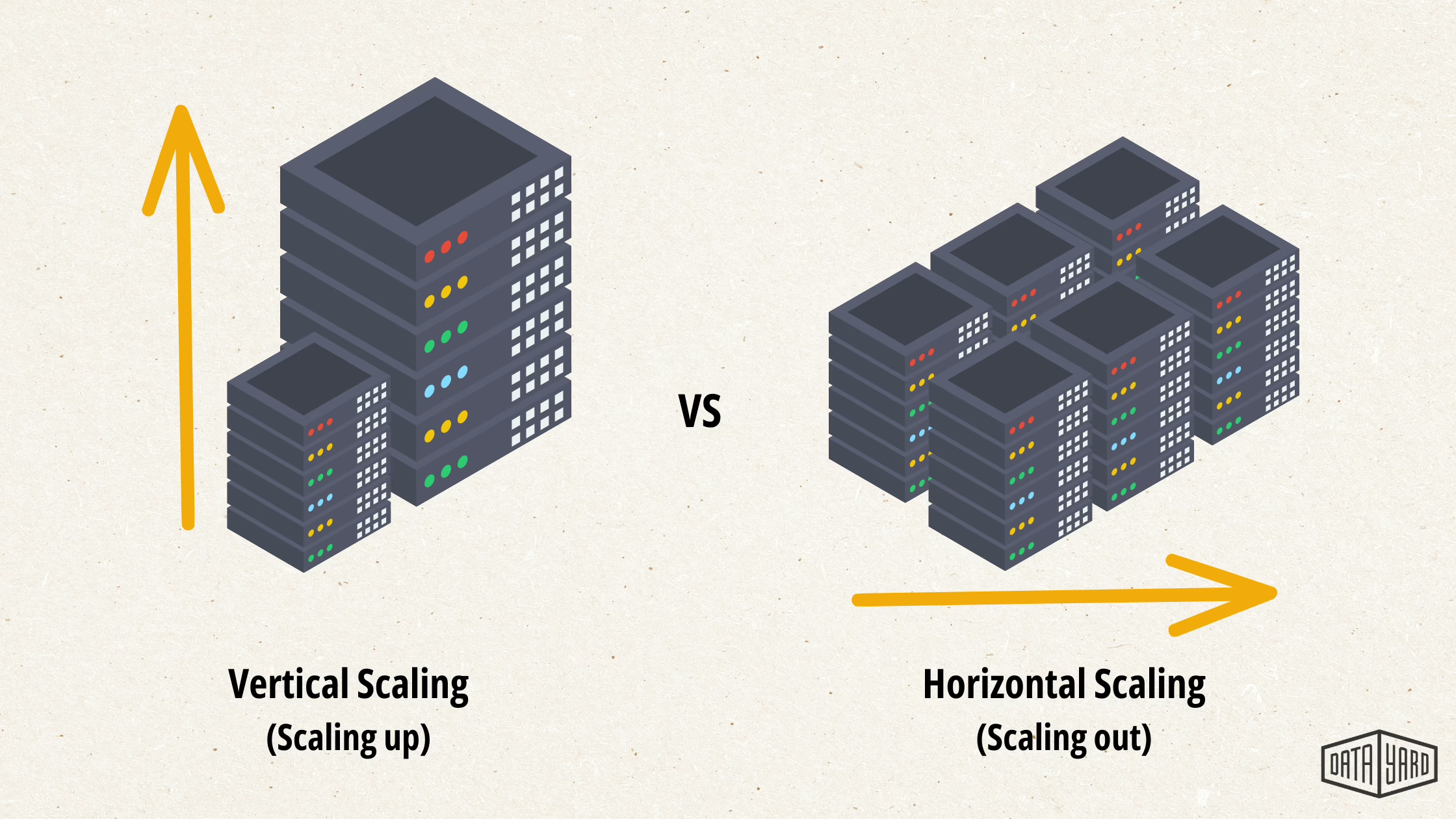
Vertical scaling means increasing the power of a single server or instance — more CPU, more memory, or faster storage. It can be simple to implement because you often don’t need to change the application. For steady, predictable workloads and some legacy databases, vertical scaling can be an efficient way to boost performance.
Some limitations: a single machine has finite capacity, upgrades may require downtime, and a hardware or instance failure can take the entire system offline. In practice, vertical scaling is best when you need short‑term capacity increases or when an application cannot be distributed across multiple servers.
Horizontal scaling adds more servers or instances and distributes traffic across them. This approach increases fault tolerance and enables potentially unlimited cloud scalability across multiple machines — ideal for handling traffic spikes and high-concurrency applications.
The trade-offs are complexity and operational overhead: you’ll need load balancing, consistent configurations across instances (immutable infrastructure or automated configuration management), and sometimes application redesign (stateless services, distributed caches, or data partitioning). Horizontal scaling commonly relies on load balancers and virtual machines or containers to add and remove compute resources on demand.
Quick Comparison Between Horizontal and Vertical Scaling:
| Feature | Vertical | Horizontal |
Complexity | Low | High |
Scalability Limit | Medium | High |
Downtime Risk | High | Low |
Fault Tolerance | Low | High |
When to choose which: use vertical scaling for resource-heavy, monolithic databases or systems that are hard to distribute; use horizontal scaling for front-end services, APIs, and user-facing applications where you can run many instances across zones and balance load. Many teams adopt a hybrid approach — vertical scaling for certain legacy systems and horizontal scaling for new services — combined with caching and database replicas to optimize performance and costs.
Example (vendor-neutral): to handle a promotional spike, you might vertically scale a database instance for faster writes while horizontally scaling application instances behind load balancers and warming caches. That combined approach keeps latency low, distributes load, and improves availability without unnecessary over-provisioning.
Forecast-based scaling uses historical data and business event planning to anticipate demand and provision cloud resources before traffic spikes hit, reducing latency and avoiding emergency firefights that reactive auto-scaling alone can’t always prevent.
How it works (simple checklist):
1. Forecast – model expected traffic based on past patterns, marketing calendars, and product launches.
2. Provision – schedule additional instances, storage, or database replicas 12–48 hours ahead, depending on boot and warm-up times.
3. Warm – prime caches, CDNs, and connection pools so user-facing systems serve traffic immediately.
Typical events to plan for: product launches, paid marketing campaigns, seasonal sales, or large news events — anything that predictably increases demand for a known period of time.
At DataYard, we take this forecast-based approach with our clients — using real traffic patterns to scale environments based on those predictions. You get performance where it matters, without overbuilding your stack.
Not every hosting setup supports true scalability. Here’s a high-level look at the differences:

Dedicated resources and controlled environments make the private cloud ideal for steady core workloads and compliance-sensitive systems. Use a private cloud environment as your stable base and push overflow to public providers when needed.
Public cloud platforms provide elastic compute and global networks that make rapid scaling and data distribution straightforward — but they can be costly to run all workloads here, all the time — often resulting in surprise overages.
A hybrid approach uses the private cloud for predictable baseline workloads, and scales to the public cloud for overflow and global reach. This architecture balances performance, security, and cost — a common and effective pattern for businesses planning scalable cloud services.
Scalable cloud services aren’t just for massive tech firms. Any organization that needs reliable availability, predictable performance, and better control over cloud costs should consider a scalable approach. Typical use cases include:
Marketing agencies running high-traffic campaigns or micro sites that suddenly spike traffic and need temporary additional cloud capacity.
Manufacturers with dealer portals, configurators, or inventory systems that must stay responsive during peak business hours.
Professional services firms operating secure client portals that require consistent uptime and controlled latency.
Transaction-heavy platforms (lottery systems, ticketing, e‑commerce checkout engines) that experience burst activity and can’t tolerate errors during peaks.
Any Business that sees a spike in traffic each year and needs their website, app, or platform to adjust to those traffic spikes.
In each case, the business need is the same: stay online, stay secure, and deliver fast user experiences when it matters most.
As your business grows, your technology should grow with the it — scalable cloud services make sure your infrastructure never holds you back. Here are four benefits of scaling your cloud (when you need to).

 Stay Online When It Counts
Stay Online When It Counts Downtime during a campaign or event frustrates users and kills revenue. Scalable cloud infrastructure maintains availability and performance under pressure by planning and adding capacity where and before it’s needed most, to help protect conversions and customer trust.
 Control Cloud Costs With Right-Sized Capacity
Control Cloud Costs With Right-Sized Capacity By forecasting demand and provisioning temporary resources for known peaks, you avoid keeping peak-capacity running all the time.
Example: a forecasted burst for a weekend sale can be handled with short-term public cloud instances and CDNs, which reduces the monthly infrastructure costs compared to 24/7 over-provisioning.
 Grow Without Rebuilding Everything
Grow Without Rebuilding Everything A scalable architecture grows with your needs — adding load-balanced instances, storage, or network capacity without a major rebuild. That means quicker launches, less engineering rework, and lower long-term costs.
 Performance & User Experience — Measurable Gains
Performance & User Experience — Measurable Gains Improved availability reduces 500 errors and timeouts; better resource allocation lowers latency. For example, clients moving to a hybrid scalable model often see page-load improvements and a measurable reduction in error rates during campaigns (results vary — be sure to run a load test to set expectations).
In August 2023, the MegaMillions jackpot reached $1.602 billion and the site experienced an extraordinary surge. Over 4.26 million visitors accessed the site in a ten-minute window, generating peak traffic of nearly 10,000 requests per second.
The outcome:
How We Prepared — Forecast-Based Scaling Instead of Panic
We modeled traffic growth from jackpot announcements and known user behavior, then executed a multi-step scaling plan in the days leading up to the peak:
Cost-note: provisioning temporary public cloud resources for a forecasted peak is typically far less expensive than running equivalent peak capacity continuously. Exact savings depend on workload mix and instance types.
The takeaway: Planned and measured scaling across the right cloud platforms and services kept the site available and performant — demonstrating how cloud scalability and proactive resource management help protect the user experience under extreme load.
Take a look at the prompts below — if more than two apply to your organization, it may be helpful to evaluate cloud scalability for your environment.
Your site slows during traffic spikes
Implication: poor performance = lost conversions; action: run a load test and identify bottlenecks.)
You’ve had outages during launches or campaigns
(Implication: availability risk; action: implement redundancy and forecasted scaling.)
You’re stuck on shared hosting or rigid infrastructure
(Implication: limited ability to add resources; action: evaluate hybrid or public cloud options.)
You’re reactive, not proactive about performance
(Implication: firefighting increases costs and risk; action: set monitoring thresholds and a forecasted scaling plan.)
You’re unsure what your infrastructure is costing you
(Implication: hidden cloud costs; action: run a cost audit and model burst vs baseline expenses.)
If two or more of the items above match your situation, schedule a free consultation with our cloud experts to get your scalable cloud services set up.

Reality: Even a few hundred unexpected visitors can overwhelm a poorly architected system.
Tip: run a small load test to see at what point your pages slow or error — that’s your scalability threshold.
Reality: Using a public cloud platform doesn’t guarantee good scaling — configuration, architecture, and cost controls matter.
Tip: verify your auto-scaling policies, instance types, and cost alerts; misconfigured auto-scaling can still lead to poor performance or surprise bills.
Reality: Instant auto-scaling helps, but for many businesses, a forecast-based scaling approach (provisioning capacity before known peaks) can be more reliable and cost-effective.
Tip: combine monitoring-driven auto-scaling with scheduled, forecasted provisioning for big events.
Practical tools: use cloud provider cost reports, metrics (CloudWatch/Azure Monitor), APM (New Relic, Datadog), and simple load tests to establish baseline performance and costs.
Tip: Build simple cost models comparing forecasted burst (short-term public cloud instances + CDN) vs always-on capacity to identify breakeven points.
Example architecture (concise): private cloud for core DB and internal APIs; public cloud auto-scaling groups across multiple regions for front-end web servers; Cloudflare or CDN in front for caching and DDoS protection; managed databases with read replicas and caching tier to reduce load.
Monitoring and APM tools to consider: CloudWatch / Azure Monitor, Datadog, New Relic, Prometheus + Grafana. Use provider cost dashboards to track spend during tests.
Best practices recap: design for horizontal scaling, use CDNs and caching to reduce backend load, monitor key metrics and set alerts, run realistic load tests, and model costs for forecasted bursts versus baseline capacity.
We aren’t a hyper-scaler — we’re a hands-on cloud partner. From hybrid architecture, to forecasted scaling, to live support, we help you scale smart and stay online — when it matters most.
📅 Book Your Free Assessment
📞 Or call: 937-226-6896
📩 Email: [email protected]
Scalability isn’t a luxury — it’s your defense against downtime, slowdowns, and blown budgets.
With the right architecture and a bit of forecasting, you can scale smarter, save money, and stay available when the pressure’s on.
A: Cloud-based infrastructure and management that grows or shrinks based on demand — combining the right architecture, monitoring, and resource controls so your systems stay available without overspending.
A: A hybrid setup where core databases run on private cloud while front-end servers scale out to a public cloud during peaks, fronted by a CDN for edge caching. (See our MegaMillions case study for a high‑traffic example.)
A: Without scalability, traffic surges can cause slow load times, page errors, or outages that damage customer trust and revenue. Scalable cloud services protect availability, performance, and your bottom line.
A: Auto-scaling reacts to live usage (useful for unexpected bursts). Forecasted scaling provisions resources ahead of known events (product launches, campaigns) — often delivering better cost control and readiness for planned peaks. Best practice: combine both.
A: Yes. Both providers offer the building blocks (compute, managed databases, load balancers, storage) — but effective cloud scalability depends on architecture, cost controls, and monitoring. Hybrid designs often use private clouds for steady workloads and AWS/Azure for predictable burst capacity.
A: Costs vary by workload, instance types, and data transfer. Forecast-based scaling is typically cheaper than running peak resources 24/7.
A: Start with an audit: collect 14 days of cloud metrics, run a basic load test, and model your forecasted peaks.
CloudZero. Horizontal vs. vertical scaling: What’s the difference? CloudZero. https://www.cloudzero.com/blog/horizontal-vs-vertical-scaling/

Credit unions and other financial institutions are facing growing pressure
Cloud cost optimization in 2026 isn’t just about cutting spend

Phishing remains one of the most dangerous cyber threats facing